Choosing the right payroll approach can significantly impact your business’s efficiency, compliance, and overall costs. In today’s competitive landscape, many organizations debate between Direct Payroll vs Third-Party Payroll to determine which method best aligns with their operational needs. While direct payroll offers control and transparency, outsourcing to a third-party can save time and reduce administrative burdens. This article breaks down the core differences, advantages, and challenges of each option to help you decide which payroll model is the smarter fit for your business.
What Is Direct Payroll?
Direct payroll refers to an in-house payroll system managed by the company’s HR or finance team. The organization is responsible for calculating wages, tax deductions, benefits administration, and compliance with labor laws. Using direct payroll allows businesses to maintain full control over payroll processes and data.
Advantages of direct payroll:
- Control and Customization: Companies can tailor payroll operations to meet unique needs, making direct adjustments quickly.
- Data Security and Confidentiality: With payroll data stored internally, risks associated with external data breaches can be minimized.
- Integration with Internal Systems: Direct payroll often integrates seamlessly with existing accounting and HR systems.
Challenges of direct payroll Companies:
- Resource Intensive: Managing payroll requires dedicated staff with expertise in tax laws and payroll regulations.
- Compliance Risks: Keeping up with ever-changing legal requirements can be complex, increasing the risk of errors.
- Technology Investment: Companies must invest in payroll software and maintain updates.
Higher operational responsibility your team must stay updated on tax codes and compliance rules.

What Is Third-Party Payroll?
Third-party payroll involves outsourcing payroll functions to external payroll companies or payroll service providers. These specialists handle wage calculations, tax filings, compliance, and sometimes broader HR functions, often under the umbrella of outsourced HR services.
Advantages of third-party payroll:
- Expertise and Compliance: Payroll companies stay updated with regulatory changes, reducing compliance risks.
- Cost Efficiency: Outsourcing may reduce overhead costs by eliminating the need for dedicated payroll staff and software.
- Time Savings: Allows internal teams to focus on core business activities instead of administrative tasks.
- Scalable Solutions: Payroll service providers can easily accommodate organizational growth and complexity, including global payroll management.
Challenges of third-party payroll:
- Less Direct Control: Outsourcing means relinquishing some control over payroll processes.
- Data Security Concerns: Sharing sensitive payroll information externally requires trusting the service provider’s security measures.
- Vendor Dependency: Businesses may face challenges if the provider experiences issues or service interruptions.
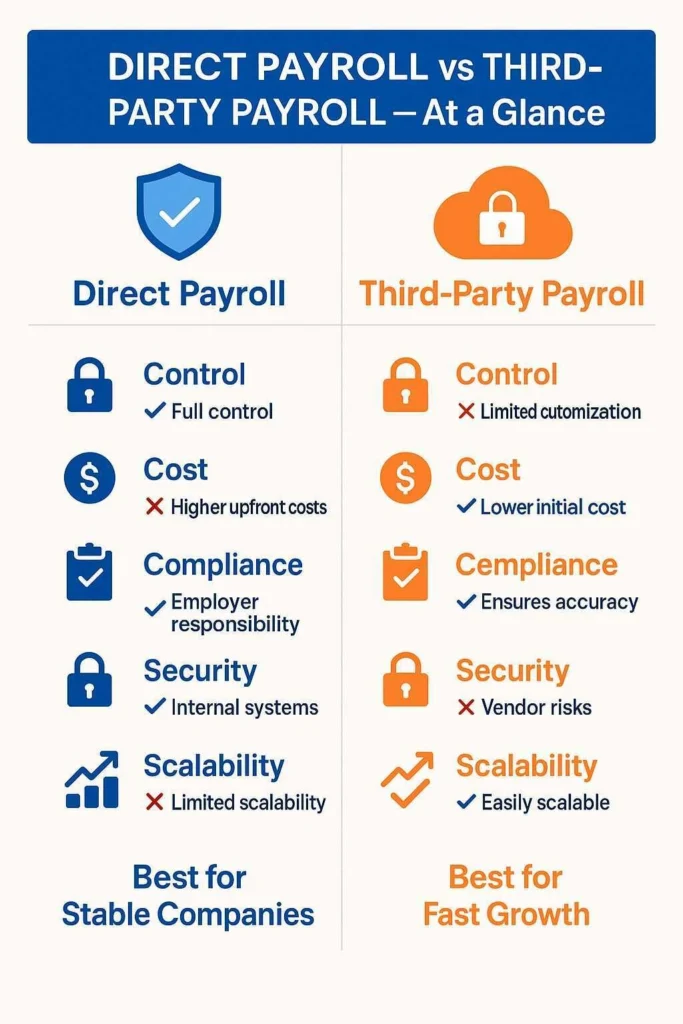
Direct Payroll vs Third-Party Payroll: A Side-by-Side Comparison
| Factor | Direct Payroll (In-House) | Third-Party Payroll (Outsourced) |
| Control & Transparency | Full control over data, instant issue resolution | Limited customization, SLA-driven processes |
| Cost Structure | Higher upfront costs, potential long-term efficiency | Lower initial cost, but hidden fees are possible |
| Compliance | Full employer responsibility | Vendor ensures statutory accuracy |
| Data Security | Internal systems protect confidentiality | Strong vendor security, but external risks added |
| Scalability | Can strain without automation | Easily scales with provider systems |
| Employee Experience | Stronger cultural alignment, benefit integration | Risk of detachment from the employer brand |
Pros and Cons of Each Model
Direct Payroll
Pros:
- Maximum control and customization
- Strong confidentiality
- Long-term cost efficiency with stable systems
Cons:
- Requires ongoing compliance expertise
- Higher staffing and software overheads
- Scalability challenges without automation
Third-Party Payroll
Pros:
- Saves HR time and resources
- Strong compliance and tax expertise
- Scales quickly across geographies
Cons:
- Less direct control over payroll data
- Hidden fees for extra services (off-cycle runs, custom reports)
- Integration and employee experience challenges
Key Factors to Consider : Payroll vs Third-Party Payroll
- Business Size and Complexity: Small and mid-sized businesses may benefit more from outsourcing, while larger enterprises might prefer in-house control.
- Regulatory Environment: Businesses operating in multiple regions or countries might find global payroll providers essential for compliance.
- Technology and Integration Needs: Consider how payroll interfaces with other systems like HR management or accounting software.
- Cost Implications: Analyze total cost of ownership including software, staff, and potential penalties for non-compliance.
- Strategic Focus: Determine whether payroll is a core competency or better delegated to specialized providers.
When to Choose Direct Payroll
Direct payroll is a better fit if your company:
- Operates in a sensitive industry where confidentiality and control are critical.
- Has a stable workforce size with mature HR systems.
- Prioritises employee experience and cultural alignment.
When to Choose Third-Party Payroll
Third-party payroll is the right choice if your company:
- Needs to scale rapidly across regions or seasonal workforce cycles.
- Lacks in-house expertise in compliance and payroll taxation.
- Wants to free HR teams from administrative tasks to focus on strategy.
Risk Mitigation Tips
For Direct Payroll:
- Invest in robust HRMS + payroll automation.
- Schedule regular compliance audits to reduce errors.
For Third-Party Payroll:
- Audit vendor fee schedules upfront to avoid hidden costs.
- Demand strong data security certifications.
- Define SLAs with KPIs for timeliness, accuracy, and employee satisfaction.
Conclusion
There is no universal winner in the direct payroll vs third-party payroll debate.
- Direct payroll is best for companies that value control, confidentiality, and cultural integration.
- Third-party payroll is ideal for organizations prioritizing scalability, compliance, and administrative efficiency.
The smartest businesses evaluate total cost of ownership, compliance risks, and employee experience before choosing—or even adopting a hybrid payroll model.
AHS HR Solutions also provides expert payroll outsourcing, compliance management, and HR solutions to help businesses streamline their payroll and HR processes with accuracy and efficiency. check out AHS payroll outsourcing services.
For the official government resources on payroll rules and compliance in India, you can visit the Ministry of Labour & Employment website, which covers key acts such as the Payment of Wages Act, Minimum Wages Act, Employees’ Provident Fund Act, and Employees’ State Insurance Act. The official URLs include:
- Payment of Wages Act details: https://clc.gov.in/clc/acts-rules/payment-wages-0
- Labour Ministry’s Code on Wages: https://labour.gov.in/code-wages
- Labour Bureau wage-related information: https://labourbureau.gov.in/wagessection
- Income Tax rules related to payroll: https://incometaxindia.gov.in/pages/rules/income-tax-rules-1962.aspx
These sites provide comprehensive legal frameworks, rules, and updates to help businesses comply with payroll regulations.